لیست زیر شامل توابع ریاضی داخلی است که می توانید برای مثال هنگام تعریف پارامترها و متغیرها یا مستقیماً در عبارات در رابط فیزیک یا تنظیمات ویژگی استفاده کنید. نام توابع نامهای رزرو شدهای هستند که نمیتوانند برای توابع تعریفشده توسط کاربر استفاده شوند، اما میتوانند برای نام متغیرها و پارامترها استفاده شوند. این توابع واحدهایی برای آرگومان های ورودی یا خروجی خود ندارند (مگر در مواردی که برای توابع مثلثاتی ذکر شده باشد)
|
NAME
|
DESCRIPTION
|
SYNTAX
|
|
abs
|
Absolute value
|
abs(x)
|
|
acos
|
Inverse cosine (in radians)
|
acos(x)
|
|
acosh
|
Inverse hyperbolic cosine
|
acosh(x)
|
|
acot
|
Inverse cotangent (in radians)
|
acot(x)
|
|
acoth
|
Inverse hyperbolic cotangent
|
acoth(x)
|
|
acsc
|
Inverse cosecant (in radians)
|
acsc(x)
|
|
acsch
|
Inverse hyperbolic cosecant
|
acsch(x)
|
|
arg
|
Phase angle (in radians)
|
arg(z)
|
|
asec
|
Inverse secant (in radians)
|
asec(x)
|
|
asech
|
Inverse hyperbolic secant
|
asech(x)
|
|
asin
|
Inverse sine (in radians)
|
asin(x)
|
|
asinh
|
Inverse hyperbolic sine
|
asinh(x)
|
|
atan
|
Inverse tangent (in radians)
|
atan(x)
|
|
atan2
|
Four-quadrant inverse tangent (in radians)
|
atan2(y,x)
|
|
atanh
|
Inverse hyperbolic tangent
|
atanh(x)
|
|
besselj
|
Bessel function of the first kind
|
besselj(n,z)
|
|
bessely
|
Bessel function of the second kind
|
bessely(n,z)
|
|
besseli
|
Modified Bessel function of the first kind
|
besseli(n,z)
|
|
besselk
|
Modified Bessel function of the second kind
|
besselk(n,z)
|
|
binomial
|
Binomial coefficient
|
binomial(n,k)
|
|
ceil
|
Nearest following integer
|
ceil(x)
|
|
conj
|
Complex conjugate
|
conj(x)
|
|
cos
|
Cosine
|
cos(z)
|
|
cosh
|
Hyperbolic cosine
|
cosh(x)
|
|
cot
|
Cotangent
|
cot(x)
|
|
coth
|
Hyperbolic cotangent
|
coth(x)
|
|
csc
|
Cosecant
|
csc(z)
|
|
csch
|
Hyperbolic cosecant
|
csch(x)
|
|
erf
|
Error function
|
erf(x)
|
|
erfinv
|
Inverse error function
|
erfinv(x)
|
|
exp
|
Exponential function ex. That is, exp(1) is the mathematical constant e (Euler’s number)
|
exp(x)
|
|
factorial
|
Factorial of nonnegative integer
|
factorial(n)
|
|
floor
|
Nearest previous integer
|
floor(x)
|
|
gamma
|
Gamma function
|
gamma(x)
|
|
gcd
|
Greatest common divisor
|
gcd(a,b)
|
|
imag
|
Imaginary part
|
imag(x)
|
|
lcm
|
Least common multiple
|
lcm(a,b)
|
|
legendre
|
Legendre polynomial and associated Legendre polynomial of integer degree and order (see legendre for more information)
|
legendre(l,x)
legendre(l,m,x) |
|
log
|
Natural logarithm
|
log(x)
|
|
log10
|
Base-10 logarithm
|
log10(x)
|
|
log2
|
Base-2 logarithm
|
log2(x)
|
|
max
|
Maximum of two arguments
|
max(x,y)
|
|
min
|
Minimum of two arguments
|
min(x,y)
|
|
mod
|
Modulo operator
|
mod(x,y)
|
|
poweps
|
Power for use with derivatives of expressions that need to be evaluated near zero (see poweps and sqrteps for more information)
|
poweps(x,n)
|
|
psi
|
Psi function and its derivatives (psi(0,x) is the digamma function)
|
psi(k,x)
|
|
random
|
Random function, uniform distribution
|
random(x,y,…)
|
|
randomnormal
|
Random function, normal (Gaussian) distribution
|
randomnormal(x,y,…)
|
|
range
|
Create a range of numbers (see Entering Ranges and Vector-Valued Expressions)
|
range(start,step,end)
|
|
real
|
Real part
|
real(x)
|
|
round
|
Round to closest integer or to closest number with specified precision p (number of decimal digits). For negative p, round to closest integer number divisible by 10^(-p).
|
round(x)
round(x,p)
|
|
sec
|
Secant
|
sec(z)
|
|
sech
|
Hyperbolic secant
|
sech(x)
|
|
sign
|
Signum function
|
sign(x)
|
|
sin
|
Sine
|
sin(z)
|
|
sinh
|
Hyperbolic sine
|
sinh(x)
|
|
sphericaly
|
Spherical harmonic function (see sphericaly for more information)
|
sphericaly(l,m,theta,phi)
|
|
sphericalyr
|
Real spherical harmonic function (see sphericalyr for more information)
|
sphericalyr(l,m,theta,phi)
|
|
sqrt
|
Square root
|
sqrt(x)
|
|
sqrteps
|
Square root for use with derivatives of expressions that need to be evaluated near zero (see poweps and sqrteps for more information)
|
sqrteps(x)
|
|
tan
|
Tangent
|
tan(z)
|
|
tanh
|
Hyperbolic tangent
|
tanh(x)
|
|
zernike
|
Zernike polynomial function (see zernike for more information
|
zernike(n,m,r,phi)
|
افسانه
تابع legendre(l,x) یک چند جمله ای لژاندر P l ( x ) با درجه صحیح l را ارزیابی می کند :
تابع legendre(l,m,x) یک چند جمله ای Legendre مرتبط با 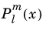 درجه صحیح l و مرتبه m را ارزیابی می کند :
درجه صحیح l و مرتبه m را ارزیابی می کند :
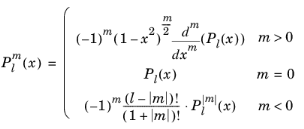
درجه l باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت غیر منفی و مرتبه m باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت باشد. برای 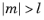 ، legendre(l,m,x) صفر را برمی گرداند.
، legendre(l,m,x) صفر را برمی گرداند.
poweps و sqrteps
توابع توان ویژه و ریشه مربع به ترتیب poweps و sqrteps زمانی مورد نیاز هستند که مشتقات عبارات باید نزدیک به صفر ارزیابی شوند. به عنوان مثال، هنگام ارزیابی نتایج یک تحلیل سیگنال کوچک و محاسبه دیفرانسیل در طول پس پردازش. خود توابع به ترتیب مقدار دقیق یا توان ( ^ ) و ریشه مربع ( sqrt ) را ارزیابی می کنند. اپسیلون فقط برای مشتقات آنها به عبارات اضافه می شود. برای عبارت poweps(x,n) = a^n ، مشتق آن نسبت به x n · ( x+eps)^(n-1) است. برای یک عبارت sqrteps(x) =sqrt(x) ، مشتق آن 0.5/sqrt(x+eps) است.
به صورت کروی
تابع کروی (l، m، تتا، فی) تابع هارمونیک کروی را ارزیابی می کند 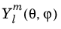 :
:
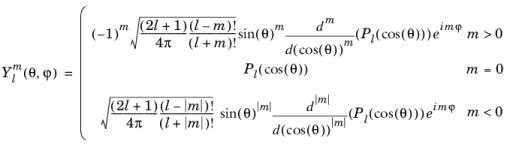
که در آن P l چند جمله ای لژاندر درجه l است. درجه l باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت غیر منفی و مرتبه m باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت باشد. برای 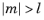 ، کروی (l، m، تتا، فی) صفر را برمیگرداند.
، کروی (l، m، تتا، فی) صفر را برمیگرداند.
کروی
تابع کروی (l، m، تتا، فی) تابع هارمونیک کروی واقعی را ارزیابی می کند 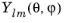 :
:
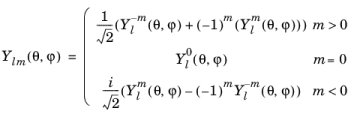
درجه l باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت غیر منفی و مرتبه m باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت باشد. برای 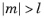 ، sphericalyr(l، m، تتا، فی) صفر را برمیگرداند. آرگومان های θ و
، sphericalyr(l، m، تتا، فی) صفر را برمیگرداند. آرگومان های θ و 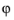 باید واقعی باشند.
باید واقعی باشند.
zernike
تابع zernike(m,n,r,phi) یک چند جمله ای Zernike 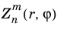 را که به شکل زیر تعریف شده است ارزیابی می کند:
را که به شکل زیر تعریف شده است ارزیابی می کند:
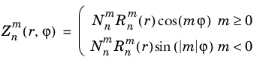
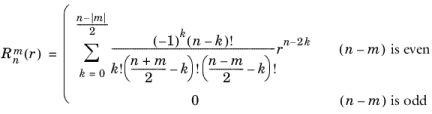
و 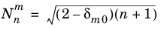 عامل عادی سازی است. آرگومان n باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت غیر منفی باشد و آرگومان m باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت رضایت بخش
عامل عادی سازی است. آرگومان n باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت غیر منفی باشد و آرگومان m باید یک عدد صحیح ثابت رضایت بخش 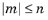 باشد. آر و آرگومان ها
باشد. آر و آرگومان ها 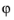 باید واقعی باشند.
باید واقعی باشند.